EVA’s latest monthly Gas and Coal Price Sensitivity Outlook indicates that annual 2019 coal burn will end up below 600 million tons while gas burn will surpass 2018 levels and end up at nearly 29 BCFD for the year. January gas burn was off to a good start with a 6.2% increase YoY, despite total electricity demand down by 5% over 2018. Coal burn slid by nearly 14% YoY and is expected to continue this trend for the balance-of-year. Exhibit 8 of the report shows that gas burn will remain high for 2019 and 2020 while coal burn will continue to slide.
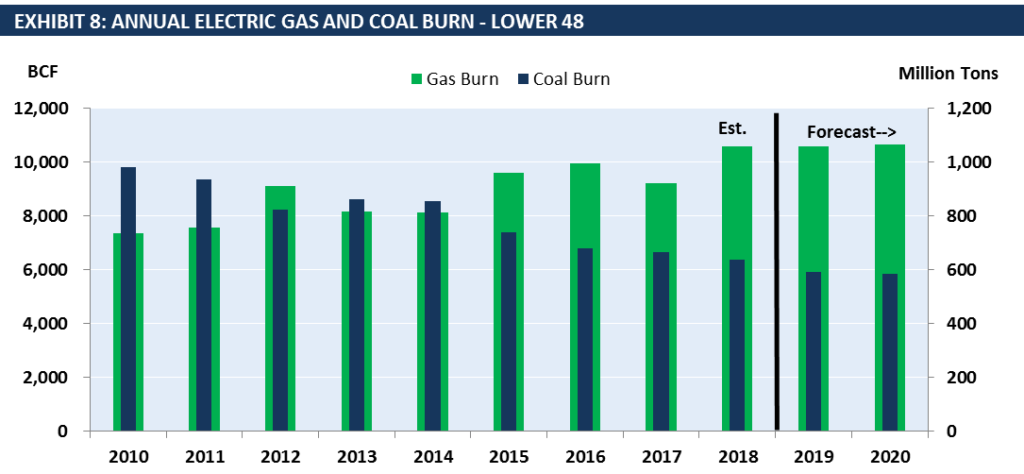
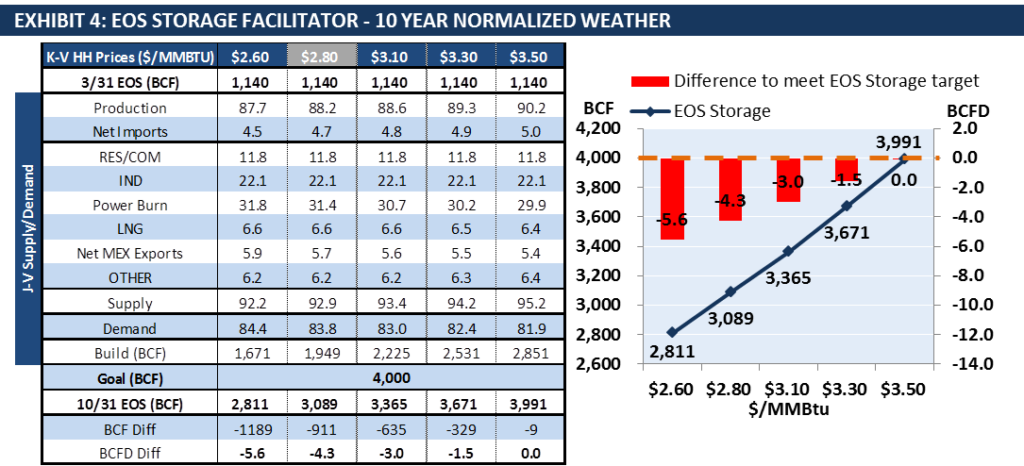
Exhibit 4 from our report highlights where the gas prices will need to be in order to achieve a 4.0 TCF storage level at the end of summer 2019. Last year’s winter walk-in storage number was 3.2 TCF, the lowest level since 2005. Despite low inventory, high production and milder winter weather allowed gas prices to remain moderate during the Nov-Mar timeframe. According to EVA’s sensitivity analysis, the 2019 winter walk-in storage number will be ~3.1 TCF, 100 BCF below last year’s level. To achieve a 4 TCF storage goal, gas prices will have to rise to $3.50/MMBTU for the remainder of summer to incentivize production and to reduce power sector gas demand.
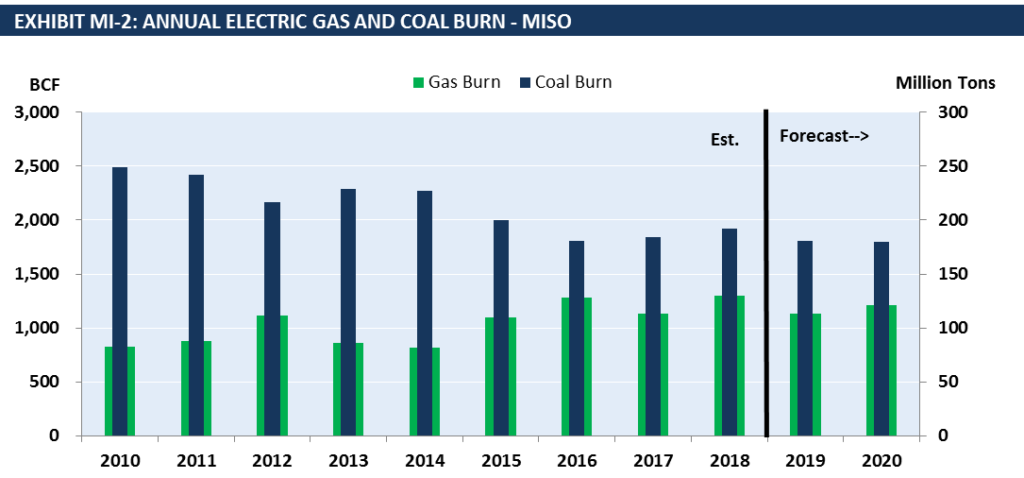
For our public release of our April report we want to highlight market dynamics in the MISO market. Since 2010 MISO has seen a consistent decline in coal burn while gas burn has followed an upward trend. Exhibit MI-2 shows that both coal and gas burn are expected to decline in 2019 compared to 2018 as electricity demand dwindles and renewables take a larger share of the generation mix.
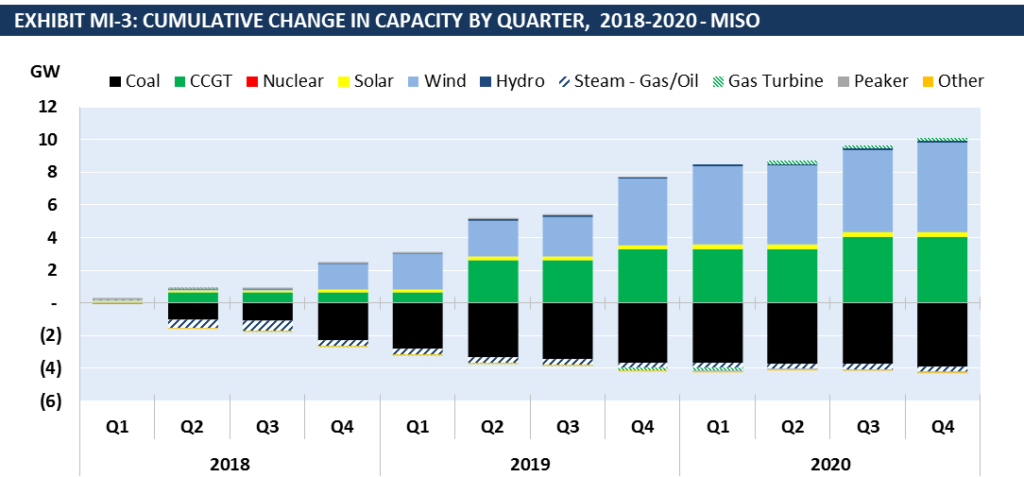
Wind capacity will continue to grow in MISO in 2019 and 2020. Coal capacity retirements will accelerate. 3.4 GW of new CCGT capacity is slated to come online by 2020 according to Exhibit MI-3 of the report.
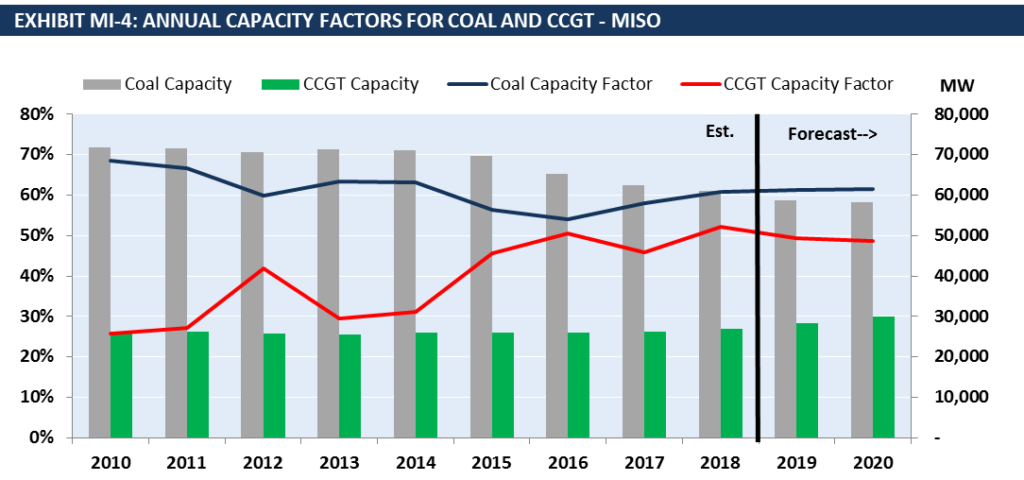
EVA’s analysis in Exhibit MI-4 shows that coal capacity factors will remain flat in 2019 and 2020, while CCGT capacity factors will decline as renewable penetration increases in MISO. Coal generation continues to hold a commanding position in MISO’s fuel-mix with ~50% market share according to 2018 annual data. Gas generation held 25% market share and wind generation accounted for 9% of total generation and continues to grow.
EVA’s monthly Gas and Coal Sensitivity Outlook combines these kinds of regional coal and gas insights with our proprietary weather-normalized price sensitivity scenario analysis. To find out more about this report and our other offerings follow the link or contact us at eva [at] evainc [dot] com.







